November 2024
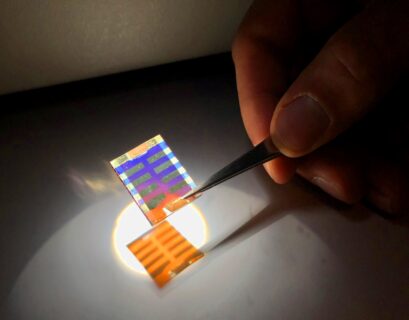
Solar cells typically base on a comparatively brittle, half-millimeter thick slice of silicon as the semiconductor. Exploiting alternative materials can provide flexibility as to the appearance of the cells such as their color, and their integration into everyday objects. Furthermore, this strategy can enable significant gains in the amount of material and energy required to build the photovoltaic device. The research cells shown here rely on a layer of antimony sulfide only 0.01% as thin as a silicon cell and are partly transparent. The solid was deposited with a precision approaching the atomic limit using a molecular chemical approach.
Research group website and Reference:
Bachmann Group: https://www.chemie.nat.fau.de/person/julien-bachmann/
Büttner et al.: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107820
